1. Introduction
General Network Infrastructure Overview
This white paper proposes a complete network architecture for the modern intelligent enterprise. The given proposal will enable the definition of general architecture suitable for the organisation’s needs now and in the future in terms of technology. Utilizing state-of-the-art networking technologies, this Best Practice Design will provide hassle-free communication to this organization and its departments to develop a platform for innovation productivity.There is it infrastructure project management with network engineers.
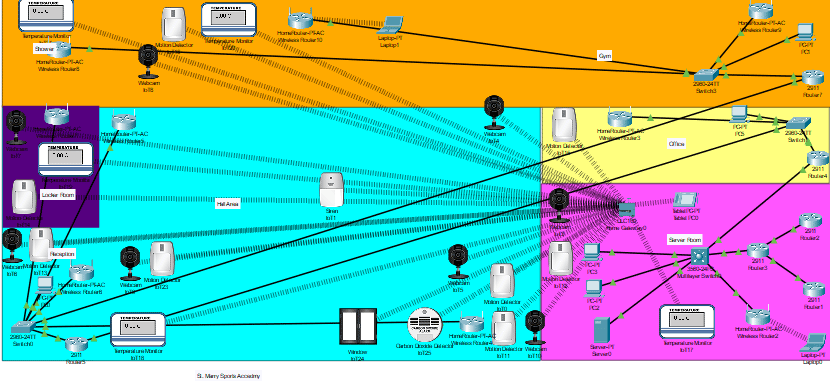
It is designed based on network infrastructure that has proper emphasis on:
•High performance, durability
•Strong security measures
•Scalability and flexibility
•New generation technologies such as Internet of Things and Cloud services
•Economy and energy saving
The primary objectives of this network infrastructure design are to:
1. Implement an effective and sound network that would enable the organization to deliver the communications and data required.
2. Put strong measures to enhance the security and safety of the network as well as the data of the network from malicious individuals.
3. To facilitate the linkage and interaction of people from one department to the other or between different sites.
4. To support scalability in the growth and expansion areas while supporting IT growth and development.
5. Mainly to enhance and balance the network and its resources.
6. To ensure the integration of smart devices and IoT systems to be successful.
7. To maintain compliance with requirements of various standards and laws prevailing in the respective industry.
2. Overview of Network Architecture
Logical Network Topology
The logical network topology is three-tiered hierarchical in design as follows:
1. Core Layer: This is the fast path of the network that is simply designed for arbitrating high speed of the fast switching framework of a dispersed network.
2. Distribution Layer: This layer accumulates connections from the access layer where policy-based connectivity is offered. The distribution layer addresses routing, filtering, and QoS policies.
3. Access Layer: It connects end-user devices and gives access to network resources.
It has the following advantages in its design:
•Scalability
•Performance by segregating traffic
•Easy troubleshooting and management
•Reliability by redundancy
it infrastructure project management with network engineers
Physical Network Layout
The physical layout of the network is aligned with the building structure of the organization and the departmental needs. The key components are as follows:
•Server Room: Houses core network equipment, servers, and storage systems
•Wiring Closets: Spread throughout the building to house access switches and patch panels
•Workstation Areas: Open office spaces and individual offices equipped with network ports and wireless access
•Conference Rooms: Equipped with high-speed wireless access and video conferencing capabilities
•Reception and Common Areas: Provide guest Wi-Fi access
Fibre optic cabling is used for backbone connections between the server room and wiring closets, while Cat6a Ethernet cabling is used for connections to end-user devices.
3. Network Segmentation
The network is divided into separate zones to improve security, increase performance, and reduce complexity. Each zone has unique access controls and security policies.
3.1 Office Network (Yellow Zone)
The Office Network zone includes general employee workstations and computers.
Features:
• VLAN segmentation by departments
• Standard internet access with content filtering
• Shared resources, including printers and file servers
• Medium security policies
3.2 Gym Network (Orange Zone)
The Administration Network zone is assigned to HR, finance, and executive staff with access to sensitive information.
Main features:
•Strict access controls
•Increased monitoring and logging
•Encryption of communication channels
•Limited access to the internet
3.3 Server Room (Pink Zone)
The Server Room zone consists of critical infrastructure components and data storage systems.
Main features:
•Very restricted access
•Advanced intrusion detection and prevention systems
•Frequent security audits and vulnerability tests
•Redundant power and cooling systems
3.4 General Access and User Area (Cyan Zone)
This area is composed of reception, cafeteria, and guest Wi-Fi, among others.
The general features include
•Internally segmented from other networks
•Low bandwidth, access limited
•User authentication with captive portal
•Content filtering, usage monitoring
it infrastructure project management with network engineers
4. Hardware and Devices
Routers and Switches
• Core Routers: Highly performing redundant routers with enhanced routing capabilities, coupled with hardware-based encryption.
• Distribution Switches: Layer 3 switches, which can run routing protocols, QoS, and VLANs.
• Access Switches: Managed Layer 2 switches supporting PoE+ to power IP phones and wireless access points.
Servers and Storage Devices
• Application Servers: Highly performing servers hosting critical business applications.
• File Servers: Dedicated file storage servers with RAID configuration for redundancy in data storage.
• Database Servers: Optimized servers for database management systems.
• Network Attached Storage (NAS): For departmental file sharing and backups.
• Storage Area Network (SAN): For high-performance, centralized storage requirements.
User End Devices
• Desktop Computers: Standard configuration for office use.
• Laptops: For mobile workforce and remote work capabilities.
• IP Phones: VoIP phones for internal and external communication.
• Tablets: For specific roles requiring mobile access to information.
IoT and Security Cameras
• IP Cameras: High-resolution cameras for facility surveillance.
• Smart Building Systems: IoT devices for HVAC control, lighting, and energy management.
• Sensors: Different types of sensors for environmental monitoring and occupancy detection.
it infrastructure project management with network engineers
5. Communication and Connectivity
Wireless Access Points
• Enterprise-grade Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax) Access Points: All over the facility to ensure thorough wireless coverage.
• Controller-based WLAN: Centralized management and optimized roaming.
• Multiple SSIDs: Separate traffic for various user groups such as employees, guests, and IoT devices.
LAN and WAN Connectivity
• LAN: 10/40/100 Gigabit Ethernet backbone with 1 Gigabit to the desktop.
• WAN: Redundant fibre optic connections to ISPs for high-speed internet access.
• MPLS: For secure and reliable connectivity between a given number of office locations.
• VPN: Site-to-site and access VPN for secure remote connectivity.
6.Network Security
Firewalls
•Next-Generation Firewalls (NGFW): These are deployed at the network perimeter and between internal segments.
•Web Application Firewall (WAF): This is deployed to protect web-based applications from common attacks.
•Database Firewall: This is an added layer of protection for such an important database system.
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS)
•Network-based IDS: They act as guards and watchfulness and monitor all network activities for strange behavior.
•Host-based IDS: These are installed in what are referred to as system servers to monitor the operational activity.
•Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): This means that it is a central point of logging, analysis and alerting all in one.
Access Control Policies
•Role-based Access Control (RBAC): To create users to have rights of access corresponding to their function.
•Network Access Control (NAC): To control access to devices that are connecting to the network to conform to security standards.
•Multi-factor Authentication (MFA): Maintaining rights for accessing various systems or any kind of data that can be confidential from the organization.
•Single Sign-On (SSO): To ease the process of authenticating a user and allow him/her to access different applications.
7. Performance and Optimization
Traffic Management
•Quality of Service (QoS): For example, in an attempt to encourage the use of voice over IP (VoIP) and video conferencing.
•Traffic Shaping: Assists in the regulation of the flow of traffic to ensure the correct division of the bandwidth.
•WAN Optimization: Applied, to improve the performance of applications that runs on the WAN.
Load Balancing
•Server Load Balancing: Load is distributed across two or more servers so that the system can achieve better performance as it is highly available.
•Link Load Balancing: Applied to enhance the use of several WAN links.
•Global Server Load Balancing (GSLB): For delivering traffic in dispersed geographical locations that have data centers.
8. Scalability in the Future
Expansion Plans
The network infrastructure is built to accommodate future growth:
•Modular Design: Enables the creation of new network segments or adds new devices to the network with simplicity.
•Overcapacity: Core and distribution layers are provisioned with extra capacity to accommodate future growth.
•Virtualization: High utilization of server and network virtualization to make it easier to deploy new services quickly.
Upgradability
•SDN Ready: The network is built to support the implementation of SDN in the future to make the network more flexible and programmable.
• IPv6 Compatibility: All network devices and systems must be IPv6-capable, which will enable future-proof addressing.
•Emerging Technologies: Infrastructure that can enable support for 5G, edge computing, advanced AI/ML applications.
9. Conclusion
Design Summary
This elaborate network infrastructure design will provide the smart organization with a robust, secure, and scalable foundation. Key features of the design include.
1. Hierarchical network architecture that ensures high performance and reliability
2. Segmented network zones for enhanced security and management
3. State-of-the-art hardware and devices to support diverse organizational needs
4. Advanced wireless capabilities for seamless mobility and IoT integration
5. Multi-layered security against potentially emergent cyber threats
6. Optimized performance and resource usage to achieve high efficiency
7. Scalable design to grow in future or technological advancement, or changes


Leave a Reply